15-1
参考例子 code/os/10-swtimer,自己尝试实现一个软件单次触发定时器。参考下面的代码实现标准的创建定时器和删除定时器接口:
/* software timer */ struct timer { void (*func)(void *arg); void *arg; uint32_t timeout_tick; }; struct timer *timer_create( void (*handler)(void *arg), void *arg, uint32_t timeout); void timer_delete(struct timer *timer);
- 软件定时器对象列表的组织先采用简单的数组管理方式;
- 数组方式实验完成后再尝试采用链表的管理方式。为加快超时对象的搜索,要求软件定时器对象在链表中按照超时的前后顺序排序,即实现一个有序的链表。
这里数组管理方式实际上已经默认实现了,参考 10-swtimer/timer.c。可以看到,这里预先定义了一个定时器数组 timer_list,在进行 timer_create、timer_delete、timer_check 等操作都需要遍历这个数组。
使用链表进行管理的代码提交见 00c63ae。首先定义链表及节点的数据结构:
/* list */
typedef struct st_list_node {
uint32_t priority; // sort by priority
void *data;
struct st_list_node *prev;
struct st_list_node *next;
} st_list_node;
typedef struct st_list {
st_list_node *head;
st_list_node *tail;
uint32_t size;
} st_list;
接着实现链表的初始化、插入、删除等操作:
// 初始化
st_list *list_init() {
st_list *list = (st_list *)mm_malloc(sizeof(st_list));
list->head = (st_list_node *)mm_malloc(sizeof(st_list_node));
list->tail = (st_list_node *)mm_malloc(sizeof(st_list_node));
list->head->prev = NULL;
list->tail->next = NULL;
list->head->next = list->tail;
list->tail->prev = list->head;
list->size = 0;
return list;
}
// 有序插入
void list_sort_insert(st_list *list, st_list_node *node) {
if (list->head == NULL || node == NULL) {
return;
}
st_list_node *p = list->head->next;
while (p != list->tail) {
if (p->priority > node->priority) {
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
node->next = p;
node->prev = p->prev;
p->prev->next = node;
p->prev = node;
list->size++;
}
st_list_node* list_cbegin(st_list *list) {
if (list->head == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
return list->head->next;
}
// only remove node from list, not free node
void list_delete(st_list *list, st_list_node *node) {
if (list->head == NULL || node == NULL) {
return;
}
node->prev->next = node->next;
node->next->prev = node->prev;
list->size--;
}
st_list_node *list_pop_front(st_list *list) {
if (list->head == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (list->head->next == list->tail) {
return NULL;
}
st_list_node *node = list->head->next;
list->head->next = node->next;
node->next->prev = list->head;
list->size--;
return node;
}
其中用到的 mm_malloc 使用了 练习 8-1 中的实现。接着使用链表的以上接口实现定时器:
static struct st_list *list_timer = NULL;
extern void timer_load(uint32_t interval);
void list_timer_init() {
list_timer = list_init();
timer_load(CLINT_TIMEBASE_FREQ / 10);
w_mie(r_mie() | MIE_MTIE);
}
struct timer *list_timer_create(void (*handler)(void *arg), void *arg, uint32_t timeout) {
if (NULL == handler || 0 == timeout) {
return NULL;
}
spin_lock();
struct timer *t = (struct timer *)mm_malloc(sizeof(struct timer));
t->func = handler;
t->arg = arg;
t->timeout_tick = get_ticks() + timeout;
struct st_list_node *node = (struct st_list_node *)mm_malloc(sizeof(struct st_list_node));
node->data = t;
node->priority = t->timeout_tick;
list_sort_insert(list_timer, node);
spin_unlock();
return t;
}
void list_timer_delete(struct timer *timer) {
spin_lock();
struct st_list_node *node = list_timer->head;
while (node != list_timer->tail) {
if (node->data == timer) {
list_delete(list_timer, node);
mm_free(node);
mm_free(timer);
break;
}
node = node->next;
}
spin_unlock();
}
void list_timer_check() {
while (1) {
struct st_list_node *node = list_cbegin(list_timer);
if (node == NULL || node == list_timer->tail) {
break;
}
struct timer *t = (struct timer *)node->data;
if (t->timeout_tick > get_ticks()) {
break;
}
struct st_list_node *mut_node = list_pop_front(list_timer);
struct timer *mut_t = (struct timer *)mut_node->data;
if (mut_t->func != NULL) {
mut_t->func(mut_t->arg);
}
mm_free(mut_node);
mm_free(mut_t);
break;
}
}
链表定时器与数组定时器相比,可以动态分配内存,定时器的数量不再受到限制。而在定时器检查时也只需要观察链表首节点是否超时,效率更高,时间复杂度从数组定时器的 O(N) 降低到了 O(1)。不过,链表定时器在插入时为了维护顺序,需要从前往后逐个检查,效率较低,复杂度依然是 O(n)。
采用如下代码模拟定时器的插入与检查操作,简单测试链表与数组的插入与删除性能。在对链表进行测试时,因为我们实现的 mm_malloc 在分配内存时需要逐个扫描已分配的内存块,检查是否被使用,在分配大量小内存块的场景下效率很差,测试发现这里会成为瓶颈,于是改为统一为链表节点和定时器各分配一大块内存再使用。
const uint32_t MAX_TIMER = 100000;
void test_list_benchmark() {
st_list *list = list_init();
uint32_t start_time = r_rdtime();
srandx(0x12345678);
printf("start time: %d\n", start_time);
uint32_t end_time = r_rdtime();
// 统一分配
void *p_node = mm_malloc(MAX_TIMER * sizeof(st_list_node));
void *p_timer = mm_malloc(MAX_TIMER * sizeof(timer));
mm_print_blocks();
uint32_t node_idx = 0;
uint32_t timer_idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TIMER; i++) {
int timeout = randx() % 10000;
st_list_node *node = (st_list_node *)(p_node + node_idx * sizeof(st_list_node));
node_idx++;
timer *t = (timer *)(p_timer + timer_idx * sizeof(timer));
timer_idx++;
t->timeout_tick = timeout;
t->func = NULL;
t->arg = NULL;
node->priority = timeout;
node->data = t;
list_sort_insert(list, node);
if (i % (MAX_TIMER / 10) == 0) {
printf("list size: %d, ticks %u\n", list_size(list), get_ticks());
}
}
printf("list size: %d, ticks %u\n", list_size(list), get_ticks());
end_time = r_rdtime();
printf("end time: %u, cost_time: %u \n", end_time, end_time - start_time);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TIMER; i++) {
if (list_empty(list)) {
break;
}
st_list_node *node = list_pop_front(list);
if (node == NULL) {
printf("node is NULL!\n");
break;
}
timer *t = (timer *)node->data;
if (t == NULL) {
printf("t is NULL!\n");
break;
}
if (i % (MAX_TIMER / 10) == 0) {
printf("list size: %d, ticks %u\n", list_size(list), get_ticks());
}
}
printf("list size: %d, ticks %u\n", list_size(list), get_ticks());
mm_free(p_node);
mm_free(p_timer);
mm_print_blocks();
list_destroy(list);
mm_print_blocks();
end_time = r_rdtime();
printf("end time: %u, cost_time: %u \n", end_time, end_time - start_time);
}
void test_array_benckmark() {
uint32_t start_time = r_rdtime();
srandx(0x12345678);
void *array_timer = mm_malloc(MAX_TIMER * sizeof(timer));
printf("start time: %d\n", start_time);
mm_print_blocks();
// init timer
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TIMER; i++) {
timer *t = (timer *)(array_timer + i * sizeof(timer));
t->func = NULL;
t->arg = NULL;
}
printf("init timer, ticks %u\n", get_ticks());
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TIMER; i++) {
int timeout = randx() % 10000;
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_TIMER; j++) {
timer *t = (timer *)(array_timer + j * sizeof(timer));
if (t->func == NULL) {
t->timeout_tick = timeout;
t->func = void_func;
t->arg = (void *)timeout;
break;
}
}
if (i % (MAX_TIMER / 10) == 0) {
printf("add timer cnt %d ticks %u\n", i, get_ticks());
}
}
printf("after add timer, ticks %u\n", get_ticks());
// check & delete timer
for (int cur_time = 0; cur_time < 10000; cur_time++) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_TIMER; j++) {
timer *t = (timer *)(array_timer + j * sizeof(timer));
if (t->func != NULL) {
if (cur_time >= t->timeout_tick) {
// t->func(t->arg);
t->func = NULL;
t->arg = NULL;
}
}
}
if (cur_time % (10000 / 10) == 0) {
printf("check time %d ticks %u\n", cur_time, get_ticks());
}
}
printf("after check timer, ticks %u\n", get_ticks());
}
其中,randx() 函数是采用 xoshiro256** 算法实现的伪随机数函数:
struct xoshiro256ss_state {
uint64_t s[4];
} state = {{1, 2, 3, 4}};
uint64_t xoshiro256ss(struct xoshiro256ss_state *state)
{
uint64_t *s = state->s;
uint64_t const result = rol64(s[1] * 5, 7) * 9;
uint64_t const t = s[1] << 17;
s[2] ^= s[0];
s[3] ^= s[1];
s[1] ^= s[2];
s[0] ^= s[3];
s[2] ^= t;
s[3] = rol64(s[3], 45);
return result;
}
test_list_benchmark 的输出为:
list size: 1, ticks 0
list size: 10001, ticks 3
list size: 20001, ticks 12
list size: 30001, ticks 28
list size: 40001, ticks 51
list size: 50001, ticks 85
list size: 60001, ticks 127
list size: 70001, ticks 189
list size: 80001, ticks 326
list size: 90001, ticks 556
list size: 100000, ticks 885
end time: 886457106, cost_time: 886327850
list size: 99999, ticks 885
list size: 89999, ticks 885
list size: 79999, ticks 885
list size: 69999, ticks 885
list size: 59999, ticks 885
list size: 49999, ticks 885
list size: 39999, ticks 885
list size: 29999, ticks 885
list size: 19999, ticks 885
list size: 9999, ticks 885
list size: 0, ticks 885
end time: 886677799, cost_time: 886548543
可以看到,随着链表大小的增加,每次插入的耗时也在增加 (O(n)),这导致整体的插入时间复杂度为 O(n^2),如下图所示。而链表的删除则很快完成。
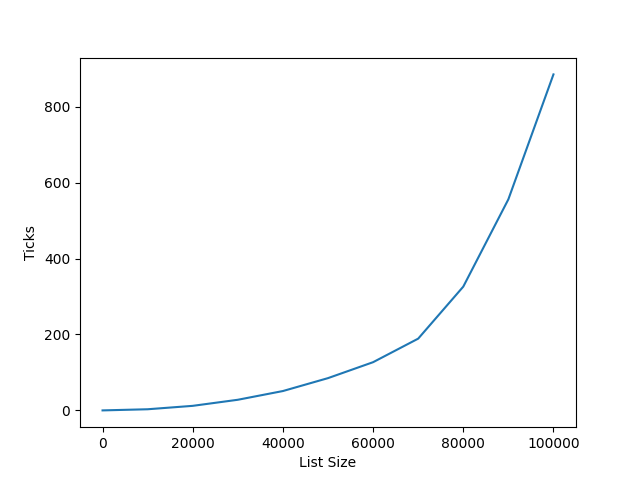
test_array_benchmark 的输出为:
init timer, ticks 0
add timer cnt 0 ticks 0
add timer cnt 10000 ticks 5
add timer cnt 20000 ticks 19
add timer cnt 30000 ticks 44
add timer cnt 40000 ticks 78
add timer cnt 50000 ticks 122
add timer cnt 60000 ticks 176
add timer cnt 70000 ticks 240
add timer cnt 80000 ticks 313
add timer cnt 90000 ticks 397
after add timer, ticks 492
check time 0 ticks 492
check time 1000 ticks 506
check time 2000 ticks 522
check time 3000 ticks 538
check time 4000 ticks 555
check time 5000 ticks 574
check time 6000 ticks 592
check time 7000 ticks 609
check time 8000 ticks 624
check time 9000 ticks 638
after check timer, ticks 649
可以看到,数组插入整体耗时要比链表少一些,不过复杂度依然是 O(n^2),且删除的速度要更慢。
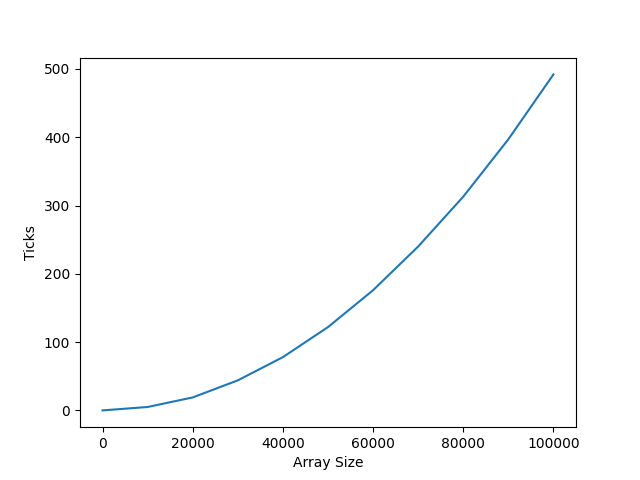
15-2
基于 练习 15-1 的有序链表实现进行进一步优化,尝试采用 跳表 (Skip List) 算法 进一步加快链表搜索的速度。 提示: 自行搜索并学习跳表算法,设置不同的层数,比较搜索的效率。
数据结构定义:
static const uint32_t INVALID = UINT32_MAX;
#define MAX_LEVEL 8
/* skip list */
typedef struct st_skip_list_node {
uint32_t priority; // sort by priority
void *data;
struct st_skip_list_node *forward[MAX_LEVEL + 1];
uint32_t level;
} st_skip_list_node;
typedef struct st_skip_list {
st_skip_list_node *head;
st_skip_list_node *tail;
uint32_t level;
uint32_t length;
} st_skip_list;
跳表的实现为:
#define MAX_LEVEL 8
void skip_list_node_init(st_skip_list_node *node, uint32_t v, uint32_t l,
void *data, st_skip_list_node *next) {
node->priority = v;
node->level = l;
node->data = data;
for (int i = 0; i <= l; i++) {
node->forward[i] = next;
}
for (int i = l + 1; i <= MAX_LEVEL; i++) {
node->forward[i] = (st_skip_list_node *)0;
}
}
st_skip_list *skip_list_init() {
st_skip_list *list = (st_skip_list *)mm_malloc(sizeof(st_skip_list));
list->head = (st_skip_list_node *)mm_malloc(sizeof(st_skip_list_node));
list->tail = (st_skip_list_node *)mm_malloc(sizeof(st_skip_list_node));
skip_list_node_init(list->tail, INVALID, 0, NULL, NULL);
skip_list_node_init(list->head, INVALID, MAX_LEVEL, NULL, list->tail);
list->level = 0;
list->length = 0;
return list;
}
int random_level() {
int level = 0;
while (randx() % 2) {
level++;
}
return level < MAX_LEVEL ? level : MAX_LEVEL;
}
void skip_list_insert(st_skip_list *list, uint32_t priority, void *data) {
if (list == NULL) {
return;
}
st_skip_list_node *update[MAX_LEVEL + 1];
st_skip_list_node *p = list->head;
for (int i = list->level; i >= 0; i--) {
while (p->forward[i]->priority < priority) {
p = p->forward[i];
}
update[i] = p;
}
p = p->forward[0];
int new_level = random_level();
if (new_level > list->level) {
for (int i = list->level + 1; i <= new_level; i++) {
update[i] = list->head;
}
list->level = new_level;
}
st_skip_list_node *new_node =
(st_skip_list_node *)mm_malloc(sizeof(st_skip_list_node));
skip_list_node_init(new_node, priority, new_level, data, NULL);
for (int i = 0; i <= new_level; i++) {
new_node->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = new_node;
}
list->length += 1;
}
int skip_list_delete(st_skip_list *list, uint32_t priority, int free_node) {
if (list == NULL) {
return 0;
}
st_skip_list_node *update[MAX_LEVEL + 1];
st_skip_list_node *p = list->head;
for (int i = list->level; i >= 0; i--) {
while (p->forward[i]->priority < priority) {
p = p->forward[i];
}
update[i] = p;
}
p = p->forward[0];
if (p->priority != priority) {
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= list->level; i++) {
if (update[i]->forward[i] != p) {
break;
}
update[i]->forward[i] = p->forward[i];
}
if (free_node) {
mm_free(p);
}
while (list->level > 0 && list->head->forward[list->level] == list->tail) {
list->level -= 1;
}
list->length -= 1;
return 1;
}
st_skip_list_node *skip_list_cbegin(st_skip_list *list) {
if (list == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
return list->head->forward[0];
}
st_skip_list_node *skip_list_pop_front(st_skip_list *list) {
if (list == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
st_skip_list_node *node = list->head->forward[0];
if (node == list->tail) {
return NULL;
}
skip_list_delete(list, node->priority, 0);
return node;
}
使用跳表的以上接口实现的定时器:
static st_skip_list *skip_list_timer = NULL;
void skip_list_timer_init() {
skip_list_timer = skip_list_init();
timer_load(CLINT_TIMEBASE_FREQ / 10);
w_mie(r_mie() | MIE_MTIE);
}
struct timer *skip_list_timer_create(void (*handler)(void *arg), void *arg, uint32_t timeout) {
if (NULL == handler || 0 == timeout) {
return NULL;
}
spin_lock();
struct timer *t = (struct timer *)mm_malloc(sizeof(struct timer));
t->func = handler;
t->arg = arg;
t->timeout_tick = get_ticks() + timeout;
skip_list_insert(skip_list_timer, t->timeout_tick, t);
spin_unlock();
return t;
}
void skip_list_timer_check() {
while (1) {
st_skip_list_node *node = skip_list_cbegin(skip_list_timer);
if (node == NULL || node == skip_list_timer->tail) {
break;
}
struct timer *t = (struct timer *)node->data;
if (t->timeout_tick > get_ticks()) {
break;
}
st_skip_list_node *mut_node = skip_list_pop_front(skip_list_timer);
struct timer *mut_t = (struct timer *)mut_node->data;
if (mut_t->func != NULL) {
mut_t->func(mut_t->arg);
}
mm_free(mut_node);
mm_free(mut_t);
break;
}
}
采用如下代码对跳表的插入删除性能进行测试:
static const uint32_t MAX_TIMER = 100000;
void test_skip_list_benchmark() {
printf("test_skip_list_benchmark\n");
printf("MAX_LEVEL: %d\n", MAX_LEVEL);
// sort insert 10000 nodes, then pop front 10000 nodes
st_skip_list *list = skip_list_init();
uint32_t start_time = r_rdtime();
srandx(0x12345678);
printf("start time: %d\n", start_time);
uint32_t end_time = r_rdtime();
// 统一分配
void *p_node = mm_malloc(MAX_TIMER * sizeof(st_skip_list_node));
void *p_timer = mm_malloc(MAX_TIMER * sizeof(timer));
mm_print_blocks();
uint32_t node_idx = 0;
uint32_t timer_idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TIMER; i++) {
int timeout = randx() % 10000;
st_skip_list_node *node = (st_skip_list_node *)(p_node + node_idx * sizeof(st_skip_list_node));
timer *t = (timer *)(p_timer + timer_idx * sizeof(timer));
node_idx++;
timer_idx++;
t->timeout_tick = timeout;
t->func = NULL;
t->arg = NULL;
node->priority = timeout;
node->data = t;
skip_list_insert2(list, node);
if (i % (MAX_TIMER / 10) == 0) {
printf("list size: %d, ticks %u, level %d\n", skip_list_size(list), get_ticks(), list->level);
}
}
// skip_list_print_level(list);
printf("list size: %d, ticks %u\n", skip_list_size(list), get_ticks());
end_time = r_rdtime();
printf("end time: %u, cost_time: %u \n", end_time, end_time - start_time);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TIMER; i++) {
if (skip_list_empty(list)) {
break;
}
st_skip_list_node *node = skip_list_pop_front(list);
if (node == NULL) {
printf("node is NULL!\n");
break;
}
timer *t = (timer *)node->data;
if (t == NULL) {
printf("t is NULL!\n");
break;
}
// mm_free(t);
// mm_free(node);
if (i % (MAX_TIMER / 10) == 0) {
printf("list size: %d, ticks %u\n", skip_list_size(list), get_ticks());
}
}
printf("list size: %d, ticks %u\n", skip_list_size(list), get_ticks());
mm_free(p_node);
mm_free(p_timer);
mm_print_blocks();
skip_list_destroy(list);
mm_print_blocks();
end_time = r_rdtime();
printf("end time: %u, cost_time: %u \n", end_time, end_time - start_time);
}
结果为:
list size: 1, ticks 0, level 0
list size: 10001, ticks 0, level 8
list size: 20001, ticks 0, level 8
list size: 30001, ticks 1, level 8
list size: 40001, ticks 1, level 8
list size: 50001, ticks 2, level 8
list size: 60001, ticks 3, level 8
list size: 70001, ticks 4, level 8
list size: 80001, ticks 6, level 8
list size: 90001, ticks 8, level 8
list size: 100000, ticks 11
end time: 11067084, cost_time: 11020391
list size: 99999, ticks 11
list size: 89999, ticks 11
list size: 79999, ticks 11
list size: 69999, ticks 11
list size: 59999, ticks 11
list size: 49999, ticks 11
list size: 39999, ticks 11
list size: 29999, ticks 11
list size: 19999, ticks 11
list size: 9999, ticks 11
list size: 0, ticks 11
这里跳表的高度为 8,插入的理论时间复杂度为 O(n*log(n)),结果符合预期。我们再测试不同高度下的情况,结果如下:
| time | 10000 | 20000 | 30000 | 40000 | 50000 | 60000 | 70000 | 80000 | 90000 | 100000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 13 | 31 | 57 | 93 | 138 | 203 | 348 | 594 | 942 |
| 1 | 1 | 7 | 16 | 30 | 49 | 85 | 169 | 303 | 487 | 719 |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | 8 | 15 | 29 | 65 | 126 | 212 | 324 | 459 |
| 3 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 21 | 47 | 85 | 137 | 199 | 274 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 14 | 30 | 52 | 79 | 112 | 150 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 10 | 19 | 31 | 46 | 64 | 85 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 11 | 17 | 25 | 34 | 45 |
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 13 | 17 | 23 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 11 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
层数到达 10 之后再增加,可以观察到耗时基本不再下降,甚至会上升,这里应该是因为每次添加节点时维护层高所需的耗时再不断增加,而因为维护层高所获得的查找时的时间复杂度收益在相对降低。
不同层高下添加节点的时间曲线:

随着层高的增加,添加 100000 节点所需的时间降低:

15-3
基于软件定时器重新实现
task_delay()。原来的task_delay()的实现十分粗糙,只是采用简单的循环来达到延时的目的,⻅下面的代码实现:void task_delay(volatile int count) { count *= 50000; while (count--); }我们希望利用调度机制,结合定时器,实现真正意义上的任务延迟(睡眠)。具体来说就是当某个任务调用
task_delay()后,内核将该任务移出调度的队列(目前的示例代码中可以认为内核只维护了一个任务调度队列),并根据任务指定的 delay 时⻓对该任务设置一个定时器,定时器到期后内核再将该任务移入调度的队列,并根据当前状态重新进行调度。建议实现后新的task_delay()接口定义如下:int task_delay(uint32_t tick);其中
tick是延迟(睡眠)的时间⻓度,单位是系统的 TICK。
实现如下:
void task_wakeup(void *arg)
{
int task_id = (int)arg;
task_status[task_id] = TASK_READY;
/* trigger a machine-level software interrupt */
int id = r_mhartid();
*(uint32_t*)CLINT_MSIP(id) = 1;
}
void task_sleep(uint32_t ticks)
{
task_status[_current] = TASK_SLEEPING;
struct timer *t = timer_create(task_wakeup, (void*)_current, ticks);
if (NULL == t) {
printf("task_sleep: timer_create failed!\n");
return;
}
/* trigger a machine-level software interrupt */
int id = r_mhartid();
*(uint32_t*)CLINT_MSIP(id) = 1;
}
新添加 task_sleep 接口来实现任务延迟,此接口将任务状态修改为 TASK_SLEEPING,此状态下任务不再进行调度;并创建一个定时器,睡眠指定的 tick 后,会调用 task_wakeup 函数唤醒此任务。而 task_wakeup 函数会将任务状态修改为 TASK_READY,重新加入调度等待队列。
我们在 os_main 函数中添加如下两个任务:
void user_task0(void* param)
{
uart_puts("Task 0: Created!\n");
while (1) {
uart_puts("Task 0: Running... \n");
// task_delay(DELAY);
task_sleep(40);
}
}
void user_task1(void* param)
{
uart_puts("Task 1: Created!\n");
while (1) {
uart_puts("Task 1: Running... \n");
// task_delay(DELAY);
task_sleep(80);
}
}
void os_main(void)
{
task_create(user_task0, 0, 0, 0);
task_create(user_task1, 0, 0, 0);
}
使用如下命令来查看 qemu 模拟器的资源占用:
top -p `ps aux | grep qemu-system | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}'`
当 user_task0 与 user_task1 均使用 task_delay 进行任务延迟时,可以看到:
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
24971 eddylu 20 0 1444804 29484 18780 S 100.3 0.1 5:00.73 qemu-system-ris
qemu 打满了一个 CPU。
我们将 task_delay 改为 task_sleep,结果为:
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
31688 eddylu 20 0 1444804 29556 18852 S 100.3 0.1 0:13.04 qemu-system-ris
CPU 依然会打满,这是因为当两个用户任务都进入 TASK_SLEEPING 状态后,由于没有用户任务可以调度,会进入内核调度任务 os_schedule:
void os_schedule(void) {
// 内核调度
while (1) {
// uart_puts("os_schedule: Activate next task\n");
int id = r_mhartid();
*(uint32_t*)CLINT_MSIP(id) = 1;
uart_puts("os_schedule: Back to OS\n");
task_delay(50000);
}
}
struct context ctx_os;
void sched_init()
{
/* init ctx_os */
ctx_os.sp = (reg_t) &stack_os[STACK_SIZE];
ctx_os.pc = (reg_t) os_schedule;
w_mscratch((reg_t)&ctx_os);
...
}
void schedule()
{
...
if (next_task_id == -1) {
// 没有可调度的任务
// printf("no schedulable task!\n");
switch_to(&ctx_os);
}
...
}
在没有可调度的任务时,会将上下文转到 ctx_os,调用 os_schedule 函数,而 os_schedule 函数再调用 task_delay,依然会占用 CPU。是否可以在 os_schedule 中调用 task_sleep 呢?这里是不太可行的。不过,可以使用 wfi 指令:
// kernel task delay using wfi instruction
void k_task_delay(volatile int count)
{
count *= 500;
while (count--) {
asm volatile("wfi");
}
}
这个指令会将 CPU 休眠,指导处理器接收到中断。我们将 os_schedule 中的 task_delay 修改为 k_task_delay,再次测试:
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
10232 eddylu 20 0 1444804 29656 18948 S 0.3 0.1 0:00.02 qemu-system-ris
CPU 终于空闲了下来。