最近看了中科大汪辰老师的 RVOS 课程视频(视频,项目),准备写一下课程的练习,在这里记录一下。
练习的代码提交到了 rvos-exercise,其中:
3-1
使用 gcc 编译代码并使用 binutils 工具对生成的目标文件和可执行文件(ELF 格式)进行分析。具体要求如下:
- 编写一个简单的打印 “hello world!” 的程序源文件:hello.c
- 对源文件进行本地编译,生成针对支持 x86_64 指令集架构处理器的目标文件 hello.o。
- 查看 hello.o 的文件的文件头信息。
- 查看 hello.o 的 Section header table。
- 对 hello.o 反汇编,并查看 hello.c 的 C 程序源码和机器指令的对应关系。
hello.c
#include "stdio.h"
int main()
{
printf("Hello World!\n");
return 0;
}
编译命令:
gcc -march=x86-64 -Wall -c hello.c -o hello.o
查看文件头信息:
readelf -h hello.o
输出为:
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: REL (Relocatable file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
Start of program headers: 0 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 600 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 0 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 0
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 14
Section header string table index: 13
查看 Section header table:
readelf -S hello.o -W
输出为:
There are 14 section headers, starting at offset 0x258:
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Address Off Size ES Flg Lk Inf Al
[ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 000000 000000 00 0 0 0
[ 1] .text PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000040 00001e 00 AX 0 0 1
[ 2] .rela.text RELA 0000000000000000 000198 000030 18 I 11 1 8
[ 3] .data PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00005e 000000 00 WA 0 0 1
[ 4] .bss NOBITS 0000000000000000 00005e 000000 00 WA 0 0 1
[ 5] .rodata PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00005e 00000d 00 A 0 0 1
[ 6] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00006b 00002c 01 MS 0 0 1
[ 7] .note.GNU-stack PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000097 000000 00 0 0 1
[ 8] .note.gnu.property NOTE 0000000000000000 000098 000020 00 A 0 0 8
[ 9] .eh_frame PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000b8 000038 00 A 0 0 8
[10] .rela.eh_frame RELA 0000000000000000 0001c8 000018 18 I 11 9 8
[11] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 0000f0 000090 18 12 4 8
[12] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 000180 000013 00 0 0 1
[13] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 0001e0 000074 00 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info),
L (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS),
C (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude),
D (mbind), l (large), p (processor specific)
反编译命令:
objdump -s -d hello.o
输出为:
hello.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Contents of section .text:
0000 f30f1efa 554889e5 488d0500 00000048 ....UH..H......H
0010 89c7e800 000000b8 00000000 5dc3 ............].
Contents of section .rodata:
0000 48656c6c 6f20576f 726c6421 00 Hello World!.
Contents of section .comment:
0000 00474343 3a202855 62756e74 75203131 .GCC: (Ubuntu 11
0010 2e342e30 2d317562 756e7475 317e3232 .4.0-1ubuntu1~22
0020 2e303429 2031312e 342e3000 .04) 11.4.0.
Contents of section .note.gnu.property:
0000 04000000 10000000 05000000 474e5500 ............GNU.
0010 020000c0 04000000 03000000 00000000 ................
Contents of section .eh_frame:
0000 14000000 00000000 017a5200 01781001 .........zR..x..
0010 1b0c0708 90010000 1c000000 1c000000 ................
0020 00000000 1e000000 00450e10 8602430d .........E....C.
0030 06550c07 08000000 .U......
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <main>:
0: f3 0f 1e fa endbr64
4: 55 push %rbp
5: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
8: 48 8d 05 00 00 00 00 lea 0x0(%rip),%rax # f <main+0xf>
f: 48 89 c7 mov %rax,%rdi
12: e8 00 00 00 00 call 17 <main+0x17>
17: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
1c: 5d pop %rbp
1d: c3 ret
3-2
如下例子 C 语言代码:
#include <stdio.h> int global_init = 0x11111111; const int global_const = 0x22222222; void main() { static int static_var = 0x33333333; static int static_var_uninit; int auto_var = 0x44444444; printf("hello world!\n"); return; }请问编译为 .o 文件后,global_init, global_const, static_var, static_var_uninit, auto_var 这些变量分别存放在那些 section 里,“hello world!\n” 这个字符串又在哪里?并尝试用工具查看并验证你的猜测。
- global_init: .data
- global_const: .rodata
- static_var: .data
- static_var_uninit: .bss
- auto_var: .text
- 字符串: .rodata
反汇编查看,命令为:
objdump -t code.o
输出:
code.o: file format elf64-x86-64
SYMBOL TABLE:
0000000000000000 l df *ABS* 0000000000000000 code.c
0000000000000000 l d .text 0000000000000000 .text
0000000000000000 l d .rodata 0000000000000000 .rodata
0000000000000000 l O .bss 0000000000000004 static_var_uninit.1
0000000000000004 l O .data 0000000000000004 static_var.0
0000000000000000 g O .data 0000000000000004 global_init
0000000000000000 g O .rodata 0000000000000004 global_const
0000000000000000 g F .text 0000000000000025 main
0000000000000000 *UND* 0000000000000000 puts
4-1
熟悉交叉编译概念,使用 riscv gcc 编译代码并使用 binutils 工具对生成的目标文件和可执行文件(ELF 格式)进行分析。具体要求如下:
- 编写一个简单的打印 “hello world!” 的程序源文件:hello.c
- 对源文件进行编译,生成针对支持 rv32ima 指令集架构处理器的目标文件 hello.o。
- 查看 hello.o 的文件的文件头信息。
- 查看 hello.o 的 Section header table。
- 对 hello.o 反汇编,并查看 hello.c 的 C 程序源码和机器指令的对应关系。
编译命令:
riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc hello.c -c -o hello.o
文件头信息:
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: REL (Relocatable file)
Machine: RISC-V
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x0
Start of program headers: 0 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 832 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x5, RVC, double-float ABI
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 0 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 0
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 12
Section header string table index: 11
Section header table:
There are 12 section headers, starting at offset 0x340:
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Address Off Size ES Flg Lk Inf Al
[ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 000000 000000 00 0 0 0
[ 1] .text PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000040 000024 00 AX 0 0 2
[ 2] .rela.text RELA 0000000000000000 000248 000090 18 I 9 1 8
[ 3] .data PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000064 000000 00 WA 0 0 1
[ 4] .bss NOBITS 0000000000000000 000064 000000 00 WA 0 0 1
[ 5] .rodata PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000068 00000d 00 A 0 0 8
[ 6] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 000075 00002c 01 MS 0 0 1
[ 7] .note.GNU-stack PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0000a1 000000 00 0 0 1
[ 8] .riscv.attributes RISCV_ATTRIBUTES 0000000000000000 0000a1 000033 00 0 0 1
[ 9] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 0000d8 000150 18 10 12 8
[10] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 000228 000020 00 0 0 1
[11] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 0002d8 000064 00 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info),
L (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS),
C (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude),
D (mbind), p (processor specific)
反汇编:
hello.o: file format elf64-littleriscv
Contents of section .text:
0000 411106e4 22e00008 17050000 13050500 A..."...........
0010 97000000 e7800000 81473e85 a2600264 .........G>..`.d
0020 41018280 A...
Contents of section .rodata:
0000 48656c6c 6f20576f 726c6421 00 Hello World!.
Contents of section .comment:
0000 00474343 3a202855 62756e74 75203131 .GCC: (Ubuntu 11
0010 2e342e30 2d317562 756e7475 317e3232 .4.0-1ubuntu1~22
0020 2e303429 2031312e 342e3000 .04) 11.4.0.
Contents of section .riscv.attributes:
0000 41320000 00726973 63760001 28000000 A2...riscv..(...
0010 05727636 34693270 305f6d32 70305f61 .rv64i2p0_m2p0_a
0020 3270305f 66327030 5f643270 305f6332 2p0_f2p0_d2p0_c2
0030 703000 p0.
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <main>:
0: 1141 addi sp,sp,-16
2: e406 sd ra,8(sp)
4: e022 sd s0,0(sp)
6: 0800 addi s0,sp,16
8: 00000517 auipc a0,0x0
c: 00050513 mv a0,a0
10: 00000097 auipc ra,0x0
14: 000080e7 jalr ra # 10 <main+0x10>
18: 4781 li a5,0
1a: 853e mv a0,a5
1c: 60a2 ld ra,8(sp)
1e: 6402 ld s0,0(sp)
20: 0141 addi sp,sp,16
22: 8082 ret
5-1
对
code/asm/sub执行反汇编,查看sub x5, x6, x7这条汇编指令对应的机器指令的编码,并对照RISC-V 的 specificaion 自己解析该条指令的编码。 现知道某条 RISC-V 的机器指令在内存中的值为b3 05 95 00,从左往右为从低地址到高地址,单位为字节,请将其翻译为对应的汇编指令。
反汇编命令:
riscv64-unknown-elf-objdump -S test.elf
结果:
test.elf: file format elf32-littleriscv
Disassembly of section .text:
80000000 <_start>:
.text # Define beginning of text section
.global _start # Define entry _start
_start:
li x6, -1 # x6 = -1
80000000: fff00313 li t1,-1
li x7, -2 # x7 = -2
80000004: ffe00393 li t2,-2
sub x5, x6, x7 # x5 = x6 - x7
80000008: 407302b3 sub t0,t1,t2
8000000c <stop>:
stop:
j stop # Infinite loop to stop execution
8000000c: 0000006f j 8000000c <stop>
可以看到 sub x5, x6, x7 对应的指令编码为 407302b3,、转化为二进制为:
4 0 7 3 0 2 b 3
------
0100 0000 0111 0011 0000 0010 1011 0011
对照 RISC-V 的 specificaion p130,可以看到这条指令对应的正是 sub x5, x6, x7。
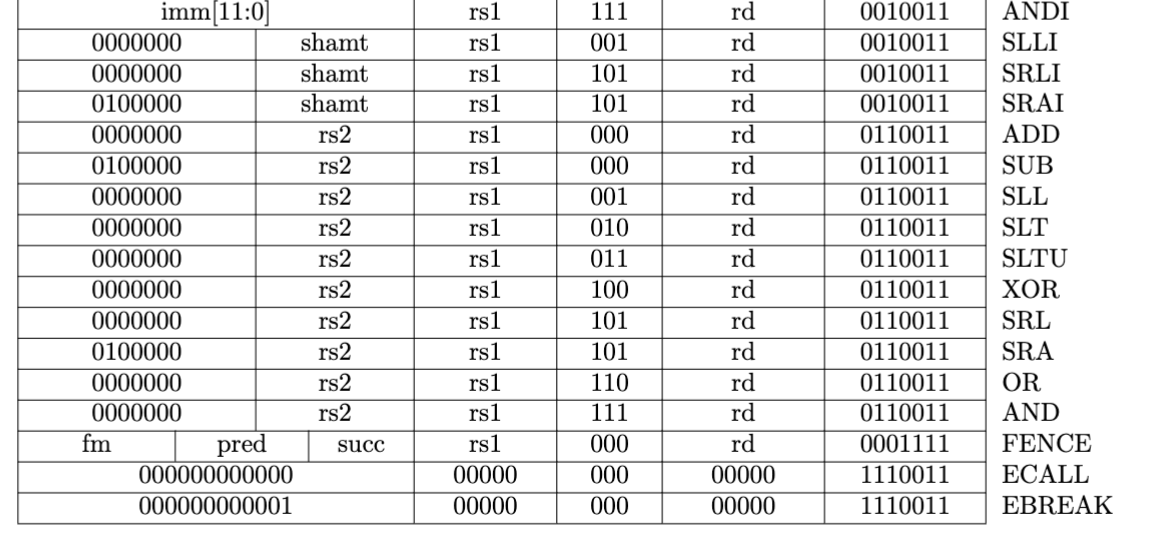
对于指令 b3 05 95 00,从左到右为低地址到高地址,因此真正的指令为 00 95 05 b3,转化为二进制为:
0 0 9 5 0 5 b 3
------
0000 0000 1001 0101 0000 0101 1011 0011
同样对照 RISC-V 的 specificaion,可以看到这条指令对应的是 add x11, x10, x9。
5-2
假设有如下这么一段 C 语言程序代码,尝试编写一段汇编代码,达到等效的结果,并采用 gdb 调试查看执行结果,注意请使用寄存器来存放变量的值:
register int a, b, c, d, e; b = 1; c = 2; e = 3; a = b + c; d = a - e;
对应的汇编代码为:
.text
.global _start
_start:
li a0, 1
li a1, 2
li a2, 3
add a3, a0, a1
sub a4, a3, a2
j _start
.end # End of file
5-3
假设有如下这么一段 C 语言程序代码,尝试编写一段汇编代码,达到等效的结果,并采用 gdb 调试查看执行结果,注意请使用寄存器来存放变量的值:
register int a, b, c, d, e; b = 1; c = 2; d = 3; e = 4; a = (b + c) - (d + e);
对应的汇编代码为:
.text
.global _start
_start:
li a0, 1
li a1, 2
li a2, 3
li a3, 4
add a4, a0, a1
add a5, a2, a3
sub a6, a4, a5
j _start
.end # End of file
5-4
给定一个 32 位数
0x87654321,先编写 c 程序,将其低 16 位 (0x4321) 和高 16 位 (0x8765) 分别分离出来保存到独立的变量中;完成后再尝试采用汇编语言实现类似的效果。
C 语言代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
unsigned int a = 0x87654321;
unsigned int low = a << 16 >> 16;
unsigned int high = a >> 16;
printf("low: %x, high: %x\n", low, high);
return 0;
}
汇编代码:
.text
.global _start
_start:
li a0, 0x87654321
slli a1, a0, 16
srli a1, a1, 16
srli a2, a0, 16
j _start
.end # End of file
5-5
假设有如下这么一段 C 代码:
int array[2] = {0x11111111, 0xffffffff}; int i = array[0]; int j = array[1];尝试用汇编语句实现等效的功能。
汇编代码:
.data
array: .word 0x11111111, 0xffffffff
.text
.global _start
_start:
la t0, array # load address of array into t0
lw a0, 0(t0) # load first element of array into a0 (i)
lw a1, 4(t0) # load second element of array into a1 (j)
j _start # Jump to _start
.end # End of file
5-6
在内存中定义一个结构体变量,编写汇编程序,用宏方式(``.macro/.endm`)实现对结构体变量的成员赋值以及读取该结构体变量的成员的值到寄存器变量中。等价的 c 语言的示例代码如下,供参考:
struct S { unsigned int a; unsigned int b; }; struct S s = {0}; #define set_struct(s) \ s.a = a; \ s.b = b; #define get_struct(s) \ a = s.a; \ b = s.b; void foo() { register unsigned int a = 0x12345678; register unsigned int b = 0x87654321; set_struct(s); a = 0; b = 0; get_struct(s); }
汇编代码:
.data
s: .word 0, 0
.macro set_struct st
la t0, \st
sw a0, 0(t0)
sw a1, 4(t0)
.endm
.macro get_struct st
la t0, \st
lw a0, 0(t0)
lw a1, 4(t0)
.endm
.text
.global _start
_start:
li a0, 0x12345678 # a = 0x12345678
li a1, 0x87654321 # b = 0x87654321
set_struct s
li a0, 0
li a1, 0
get_struct s
j _start
.end
5-7
编写汇编指令,使用条件分支指令循环遍历一个字符串数组,获取该字符串的⻓度。等价的 c 语言的示例代码如下,供参考:
char array[] = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ',', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd', '!', '\0'}; int len = 0; while (array[len] != '\0') { len++; }
汇编代码:
.data
array: .byte 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ',', 'w', 'o', 'r', 'l', 'd', '!', 0
len: .word 0
.text
.global _start
_start:
la t0, array
la t1, len
li t2, 0
loop:
lb a0, 0(t0)
beqz a0, end
addi t2, t2, 1
addi t0, t0, 1
j loop
end:
sw t2, 0(t1)
stop:
j stop
.end
5-8
阅读 code/asm/cc_leaf 和 code/asm/cc_nested 的例子代码,理解 RISC-V 的函数调用约定。在此基础上编写汇编程序实现以下功能,等价的 c 语言的示例代码如下,供参考:
unsigned int square(unsigned int i) { return i * i; } unsigned int sum_squares(unsigned int i) { unsigned int sum = 0; for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { sum += square(j); } return sum; } void _start() { sum_squares(3); }
汇编代码:
.text
.global _start
_start:
la sp, stack_end
li a0, 3
call sum_squares
addi s0, a0, 0
li a0, 4
call sum_squares
addi s1, a0, 0
stop:
j stop
sum_squares:
# prologue
addi sp, sp, -16
sw s0, 0(sp)
sw s1, 4(sp)
sw s2, 8(sp)
sw ra, 12(sp)
# body
li s0, 0 # sum
li s1, 1 # j
addi s2, a0, 0 # i
sum_sq_loop:
bgt s1, s2, sum_sq_end
addi a0, s1, 0
call square
add s0, s0, a0
addi s1, s1, 1
j sum_sq_loop
sum_sq_end:
addi a0, s0, 0
# epilogue
lw s0, 0(sp)
lw s1, 4(sp)
lw s2, 8(sp)
lw ra, 12(sp)
addi sp, sp, 16
ret
square:
# prologue
addi sp, sp, -12
sw s0, 0(sp)
sw s1, 4(sp)
sw s2, 8(sp)
# body
addi s0, a0, 0
addi s1, a0, 0
mul s2, s0, s1
addi a0, s2, 0
# epilogue
lw s0, 0(sp)
lw s1, 4(sp)
lw s2, 8(sp)
addi sp, sp, 12
ret
stack_start:
.rept 64
.word 0
.endr
stack_end:
.end
5-9
在 C 函数中嵌入一段汇编,实现 foo 函数中的
c = a * a + b * b;这句 c 语言的同等功能。int foo(int a, int b) { int c; c = a * a + b * b; return c; }
代码为:
int foo(int a, int b)
{
int c;
asm volatile(
"mul %0, %1, %1\n\t"
"mul t0, %2, %2\n\t"
"add %0, %0, t0\n\t"
: "=r"(c)
: "r"(a), "r"(b)
: "t0"
);
return c;
}
调用 foo 的汇编代码为:
.text
.global _start
.global foo
_start:
la sp, stack_end
li a0, 3
li a1, 4
call foo
mv s0, a0
stop:
j stop
nop
stack_start:
.rept 32
.word 0
.endr
stack_end:
.end